Quickstart¶
Running Server¶
Let’s first figure out how to start the external node server.
A minimal server running script looks something like this:
import mh_en_exec as mh
from nodes.foo_node import FooNode
try:
mh.exec([FooNode])
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
So what did that code do?
First we imported the Machine Heads External Node module
mh_en_execasmh.Next we imported custom node class called
FooNode. For now, let’s skip the details of creating the class, but if you want details see “Creating node class”Then we use
exec()function to execute server and wait until ends. As an argument we send list of the node classes.Also we trying to catch
KeyboardInterruptexception in order to be able stop external nodes execution by pressingCtrl+C.
Now using this code we can run the external node server.
Creating node class¶
Next, let’s see how to create your own node.
First of all, need to decide the type of the node.
Machine Heads have two type of nodes: action node and data node.
The difference is that an action node provides some operation when executed, while a data node provides data that can be used on an action node
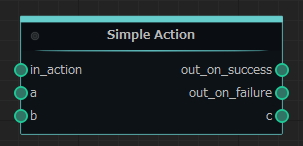
In terms of node structure, an action node has built-in “in_action” input port and “out_on_success” and “out_on_failure” output ports, and a data node has no built-in ports.
Creating data node¶
First, let’s create simple data node.
In order to do so, need to create class that will be inherited from NodeBase. It will be something like this.
# import NodeBase class
from mh_en_exec.nodes import NodeBase
# create new node class
class SimpleDataNode(NodeBase):
# set a display name
NODE_NAME = 'Simple Data'
Next, need to add ports. For this SimpleDataNode class, let’s create one string output port and name it as text.
To do so need to import StringNodeOutput
# import string output port
from mh_en_exec.nodes.ports import StringNodeOutput
And add new class variable called text, an instance of the StringNodeOutput class
# output port variable
text = StringNodeOutput()
And, finally let’s override perform function to be able return some value on the node execution.
# node execution function
def perform(self):
return ('Hello World',)
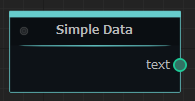
In this case SimpleDataNode will give ‘Hello World’ string value through the text output port when executed.
Final class code will be like this:
# import NodeBase class
from mh_en_exec.nodes import NodeBase
# import string output port
from mh_en_exec.nodes.ports import StringNodeOutput
# create new node class
class SimpleDataNode(NodeBase):
# set a display name
NODE_NAME = 'Simple Data'
# output port variable
text = StringNodeOutput()
# node execution function
def perform(self):
return ('Hello World',)
On “Machine Heads” node will be look like this:
Creating data node with view¶
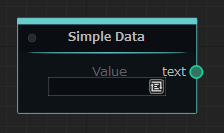
In the previous example, we made the port value hardcoded, but it is possible to make the port value set from the “Machine Heads” user interface. To do so, you need to use a port view.
Let’s try adding a port view for the text port of our previous example class SimpleDataNode. To do this, need to add a new variable named text_view, an instance of the NodeStringView, and link it to our text variable. To link, need to pass the name of the variable to which we want to link as the first argument of the NodeStringView constructor.
But first, need to import NodeStringView class.
# import string port view
from mh_en_exec.nodes.views import NodeStringView
And only after that need to add our text_view variable.
# output port variable
text = StringNodeOutput()
# output port view
text_view = NodeStringView('text')
After that, node will look like this:
Final code will be like this:
# import NodeBase class
from mh_en_exec.nodes import NodeBase
# import string output port
from mh_en_exec.nodes.ports import StringNodeOutput
# import string port view
from mh_en_exec.nodes.views import NodeStringView
# create new node class
class SimpleDataNode(NodeBase):
# set a display name
NODE_NAME = 'Simple Data'
# output port variable
text = StringNodeOutput()
# output port view
text_view = NodeStringView('text')
Note
Creating action node¶
Next, let’s create simple action node.
This time we will try to make the node add up the value of the input ports.
The formula for the operation will be as follows: a + b = c
As the last time, we start by creating a class, but this time we need to inherit ActionNodeBase class.
# import ActionNodeBase class
from mh_en_exec.nodes import ActionNodeBase
# create new node class
class SimpleActionNode(ActionNodeBase):
# set a display name
NODE_NAME = 'Simple Action'
Next, create ports. To do so, first, import IntegerNodeInput and IntegerNodeOutput
# import integer input port
from mh_en_exec.nodes.ports import IntegerNodeInput
# import integer output port
from mh_en_exec.nodes.ports import IntegerNodeOutput
and create input and output ports.
# input port variables
a = IntegerNodeInput()
b = IntegerNodeInput()
# output port variable
c = IntegerNodeOutput()
And as always need to override perform function to make some operations, but this time we will receive input port values as arguments of the perform function and return values will be not just tuple of output values, but also result of node execution.
# node execution function
def perform(self, a, b):
return True, (a + b,)
So final code will be like this:
# import ActionNodeBase class
from mh_en_exec.nodes import ActionNodeBase
# import integer input port
from mh_en_exec.nodes.ports import IntegerNodeInput
# import integer output port
from mh_en_exec.nodes.ports import IntegerNodeOutput
# create new node class
class SimpleActionNode(ActionNodeBase):
# set a display name
NODE_NAME = 'Simple Action'
# input port variables
a = IntegerNodeInput()
b = IntegerNodeInput()
# output port variable
c = IntegerNodeOutput()
# node execution function
def perform(self, a, b):
return True, (a + b,)
On “Machine Heads” this action node will be look like this: